EliA assays for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Improve the confidence of RA diagnoses with EliATM rheumatoid arthritis assays in your lab.

Why you should add EliA assays for RA to your lab.
RA is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis (IA) and early management can help slow or prevent irreversible joint destruction. Laboratories can help close the care gap by offering the full profile of tests to help improve diagnostic outcomes. Providing comprehensive testing solutions for healthcare providers helps provide patients with diagnostic answers faster.
Steps to an accurate diagnosis 1-5
Patient history and symptoms
Pre-test probability
RA specific serology testing (e.g., CCP, RF IgM, RF IgA)
Post-test probability to narrow differential
If appropriate, referral to rheumatology for further evaluation
Further evaluation
Accurate diagnosis
Patient history and symptoms
Pretest probability
RA specific serology testing (e.g., CCP, RF IgM, RF IgA)
Post-test probability to narrow differential
If appropriate, referral to rheumatology for further evaluation
Further evaluation
Accurate diagnosis
What assays are part of the EliA rheumatoid arthritis portfolio?
The EliA™ rheumatoid arthritis portfolio contains assays that detect ACPA (anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies) using CCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide) antigens as well as isotype-specific assays for rheumatoid factors (RF) IgM and IgA, all of which are recommended for a well-informed patient diagnosis. 3,6-9
When CCP, RF IgM and IgA are combined they reach nearly 100% posivite predictive vaue (PPV). 5
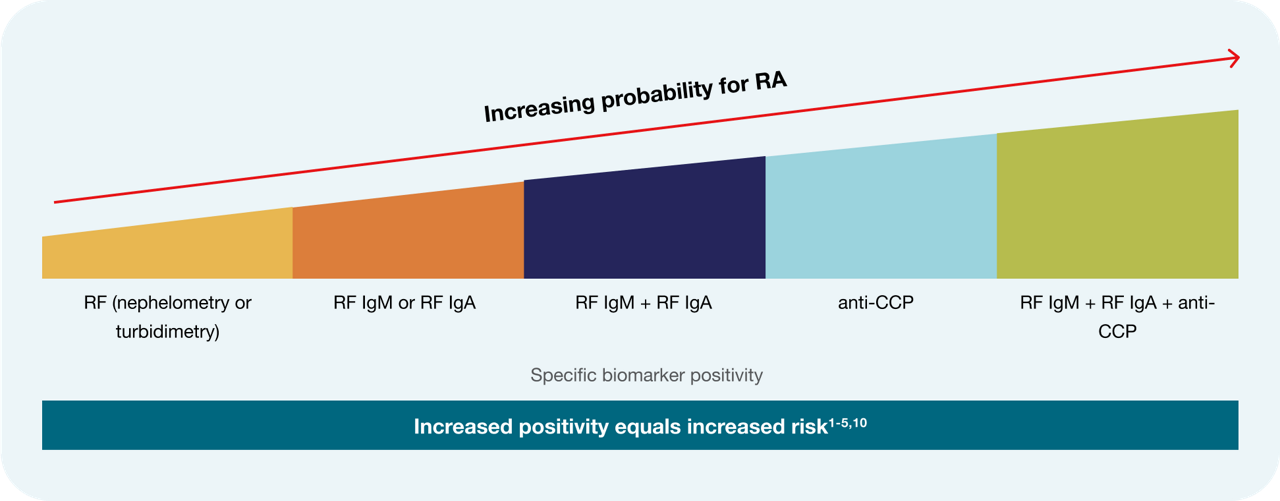
Let's break that down:
EliA CCP assay
CCP is a clinically specific marker to support in the diagnosis of RA, and its specificity for RA reduces false positive results.7
75% of initial RA testing in primary care does not include CCP. 11
Use of CCP assays helps increase the postive predictive value for testing. 5

EliA RF IgM and RF IgA assays
Combining EliATM RF IgM and EliATM RF IgA in laboratory analysis is vital in helping identify and quickly manage RA.
Less than 5% of non-RA patients are positive for both RF IgM and IgA.12
These are isotype-specific, which provides added value compared to total RF assays based on agglutination (e.g. nephelometric or turbidimetric RF assays). 12,13
Combining assays to increase RA diagnostic confidence
Testing with EliATM CCP, EliA RF IgM and EliA RF IgA assays in parallel allows you to identify patients with positivity to two or more analytes. This significantly increases the positive likelihood ratio (LR+) and the positive predictive value (PPV) of test results, as well as diagnostic confidence. 5,14,15
Become a trusted source for RA diagnotics today.
Contact us to learn more.
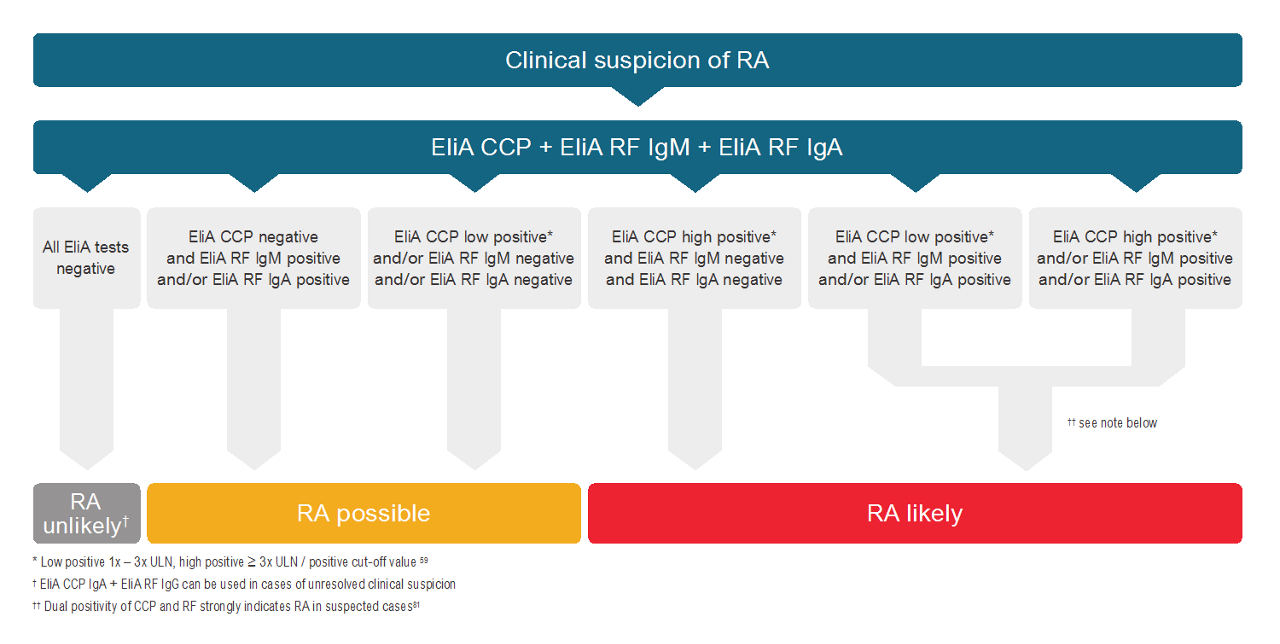
EliA rheumatoid arthritis laboratory testing algorithm
Applying a standardized testing profile with EliA assays for RA allow for convenient and efficient testing for primary care and specialists alike.
Gain the benefits of Phadia Laboratory Systems
EliA rheumatoid arthritis assays are run on PhadiaTM Laboratory Systems, including the PhadiaTM 250 instrument.

Let the Phadia 250 instrument be the backbone in maximizing your lab's workflow.
Balance of specificity and sensitivity
Antigens used in EliA™ assays are manufactured using innovative recombinant protein technology, which optimizes accessibility and purity, aiding clinicians in making impactful and appropriate decisions.16-18
High quality assays, aiding in antibody identification16-18
Even for difficult-to-detect antibodies highquality EliA™ antigens can help identify important antibodies associated with RA.5
Less false positives
High specificity due to the selection and use of recombinant antigens in this portfolio means laboratories can help reduce the number of false positives, aiding clinicians in prescribing appropriate therapies.16
Clinicians trust you. Patients depend on you.
Let us help support you.
Your partner in autoimmune diagnostics
Unlock your lab’s potential with EliA autoimmune assays and Phadia Laboratory Systems today.
- Chauhan K, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441999/
- Baker J, et al. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. UpToDate; 2024. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis
- Littlejohn EA, et al. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Prim Care. 2018;45(2):237-255.
- Jonsson T, et al. Elevation of only one rheumatoid factor isotype is not associated with increased prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis: a population based study. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000;29(3):190-191.
- Jaskowski TD, et al. Relationship Between Rheumatoid Factor Isotypes and IgG Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(8):1582-1588.
- Aletaha D, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569-2581.
- van Venrooij WJ, et al. Anti-CCP antibodies: the past, the present and the future. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(7):391-398.
- de Brito Rocha S, et al. Clinical and pathophysiologic relevance of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Rheumatol. 2019;59:2.
- Bizzaro N, et al. Antibodies to citrullinated peptides: a significant step forward in the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45(2):150-157.
- Taylor P, et al. A Systematic Review of Serum Biomarkers Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide and Rheumatoid Factor as Tests for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmune Dis. 2011;2011:815038.
- Joy V, et al. Leveraging Real World Data to Identify Addressable Diagnostic Care Gaps in Rheumatoid Arthritis, In: International Congress on Autoimmunity; 2022.
- Jónsson T, et al. Combined elevation of IgM and IgA rheumatoid factor has high diagnostic specificity for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1998;18(3):119-122.
- Bas S, et al. Comparative study of different enzyme immunoassays for measurement of IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(6):505-510.
- Sieghart D, et al. Determination of Autoantibody Isotypes Increases the Sensitivity of Serodiagnostics in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:876.
- Internal Study. Data on File
- Orme ME, et al. A comparison of a fluorescence enzyme immunoassay versus indirect immunofluorescence for initial screening of connective tissue diseases: Systematic literature review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(4):521-534.
- van der Pol P, et al. Analytical and clinical comparison of two fully automated immunoassay systems for the detection of autoantibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;476:154-159.
- Alsaed OS, et al. Clinical utility of ANA-ELISA vs ANA-immunofluorescence in connective tissue diseases. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):8229.




